As electrical systems grow increasingly complex, the likelihood of encountering electrical short circuits rises as well. These short circuits can cause various issues, ranging from minor annoyances to catastrophic failures. Fortunately, a comprehensive understanding of electrical short circuits can empower individuals with the knowledge to effectively troubleshoot and resolve these issues, ensuring the safety and reliability of electrical systems. This article presents "The Ultimate Guide to Troubleshooting Electrical Short Circuits," providing a roadmap to help you navigate the complexities of electrical short circuits and restore your systems to optimal functionality.

Understanding Electrical Short Circuits - Golden Electrical Services - Source goldenelectricalservice.com
Editor's Note: "The Ultimate Guide to Troubleshooting Electrical Short Circuits" is a valuable resource for homeowners, maintenance personnel, electricians, and anyone responsible for maintaining electrical systems. Published today, this guide empowers readers with the knowledge and techniques to confidently troubleshoot and resolve electrical short circuits.
Our team has meticulously analyzed and synthesized information from various sources, including industry-leading publications, expert insights, and practical experiences. This comprehensive guide consolidates our findings into a single, easy-to-follow resource. We have structured this guide to provide a clear and systematic approach to troubleshooting electrical short circuits, ensuring that readers can effectively identify and rectify these issues.
Key Differences:
| The Ultimate Guide to Troubleshooting Electrical Short Circuits | Other Troubleshooting Guides | |
|---|---|---|
| Scope | Provides a comprehensive overview of troubleshooting electrical short circuits for various applications. | May focus on specific types of electrical systems or components. |
| Method | Employs a systematic and step-by-step approach to troubleshoot electrical short circuits. | May offer limited guidance or rely on trial-and-error methods. |
| Analysis | Incorporates detailed analysis of potential causes and mitigation strategies. | May provide superficial or incomplete explanations. |
| Safety | Prioritizes safety precautions and safe troubleshooting practices. | May overlook safety considerations. |
| Accessibility | Written in a clear and concise style, accessible to a wide range of readers. | May be overly technical or jargon-heavy. |
Transition to Main Article Topics:
FAQ
This FAQ section addresses common queries and misconceptions regarding electrical short circuits, providing valuable insights and guidance for effective troubleshooting.
Question 1: What are the telltale signs of an electrical short circuit?
Short circuits often manifest through various symptoms, including flickering or dimming lights, tripped circuit breakers or blown fuses, burning smells, and discoloured or charred electrical outlets or wires.
Question 2: How can I safely identify the location of a short circuit?
To locate the circuit affected by the short circuit, systematically isolate and test each circuit using a non-contact voltage tester. Once the faulty circuit is identified, further inspection is necessary to pinpoint the exact location of the short.
Question 3: What are the potential causes of electrical short circuits?
Short circuits can arise from various factors, such as damaged insulation, loose electrical connections, faulty appliances or wiring, and water or moisture ingress. Identifying the root cause is crucial for preventing future occurrences.
Question 4: How do I differentiate between a short circuit and an overload?
An overload occurs when a circuit is drawing more current than it can safely handle, while a short circuit involves an unintended low-resistance path that allows excessive current to flow. Overloads typically trip circuit breakers or blow fuses, whereas short circuits can cause more severe damage.
Question 5: What precautions should I take when troubleshooting electrical short circuits?
Electrical troubleshooting should always be approached with caution. Turn off the power at the main breaker panel, wear appropriate protective gear, and use insulated tools. Never attempt to repair live wires or bypass safety mechanisms.
Question 6: When should I seek professional assistance for electrical short circuit troubleshooting?
If the short circuit persists after isolating the affected circuit, involves significant damage, or poses a potential safety hazard, it is advisable to contact a qualified electrician for further diagnosis and repairs.
By understanding these fundamental principles and following safety precautions, individuals can effectively troubleshoot electrical short circuits and ensure the safety of their electrical systems.
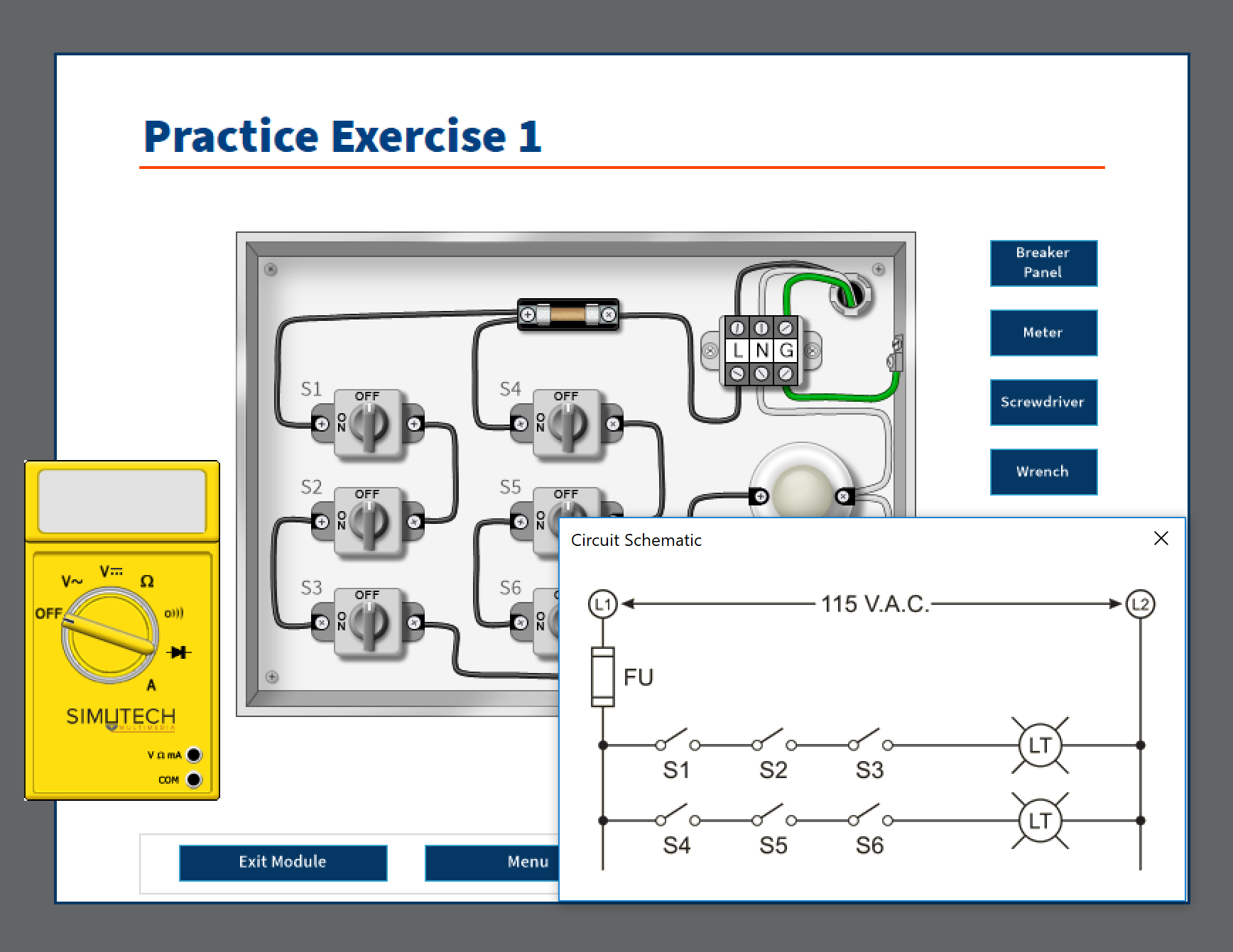
Troubleshooting Electrical Circuits (TEC) | Simutech Multimedia - Source www.simutechmultimedia.com
Tips
Avoidable hazards are present. Follow these electrician-approved tips to avoid shocks and malfunctions. Learn the The Ultimate Guide To Troubleshooting Electrical Short Circuits and enjoy a safer, more efficient home.
Tip 1: Identify the Problem
Know the exact issue and location of the short circuit. Observe blown fuses or tripped circuit breakers, flickering lights, burning odors, or smoke.
Tip 2: Safety First
Wear insulated gloves, eye protection, and turn off power at the source. Use a voltage tester to confirm the circuit is dead.
Tip 3: Check Wiring and Connections
Use a multimeter to check for continuity in wires and connections. Tighten loose wires, replace damaged ones, and secure all connections.
Tip 4: Inspect Appliances and Fixtures
Unplug appliances and disconnect fixtures from the circuit. Examine cords, plugs, switches, and wiring for any damage or wear.
Tip 5: Rule Out Ground Faults
Use a ground fault circuit interrupter (GFCI) tester to check for ground faults. GFCIs are essential for areas like bathrooms and kitchens.
Tip 6: Seek Professional Help
If troubleshooting fails, consulting a licensed electrician is necessary. They have the expertise and tools to locate and repair complex short circuits safely.
By implementing these preventive measures, you can prevent electrical short circuits, ensuring a safer and more reliable electrical system in your home.
The Ultimate Guide To Troubleshooting Electrical Short Circuits
Electrical short circuits can pose significant electrical hazards and service disruptions within various electrical systems. This comprehensive guide will explore the key aspects that aid in troubleshooting electrical short circuits effectively, ensuring electrical safety and system functionality.
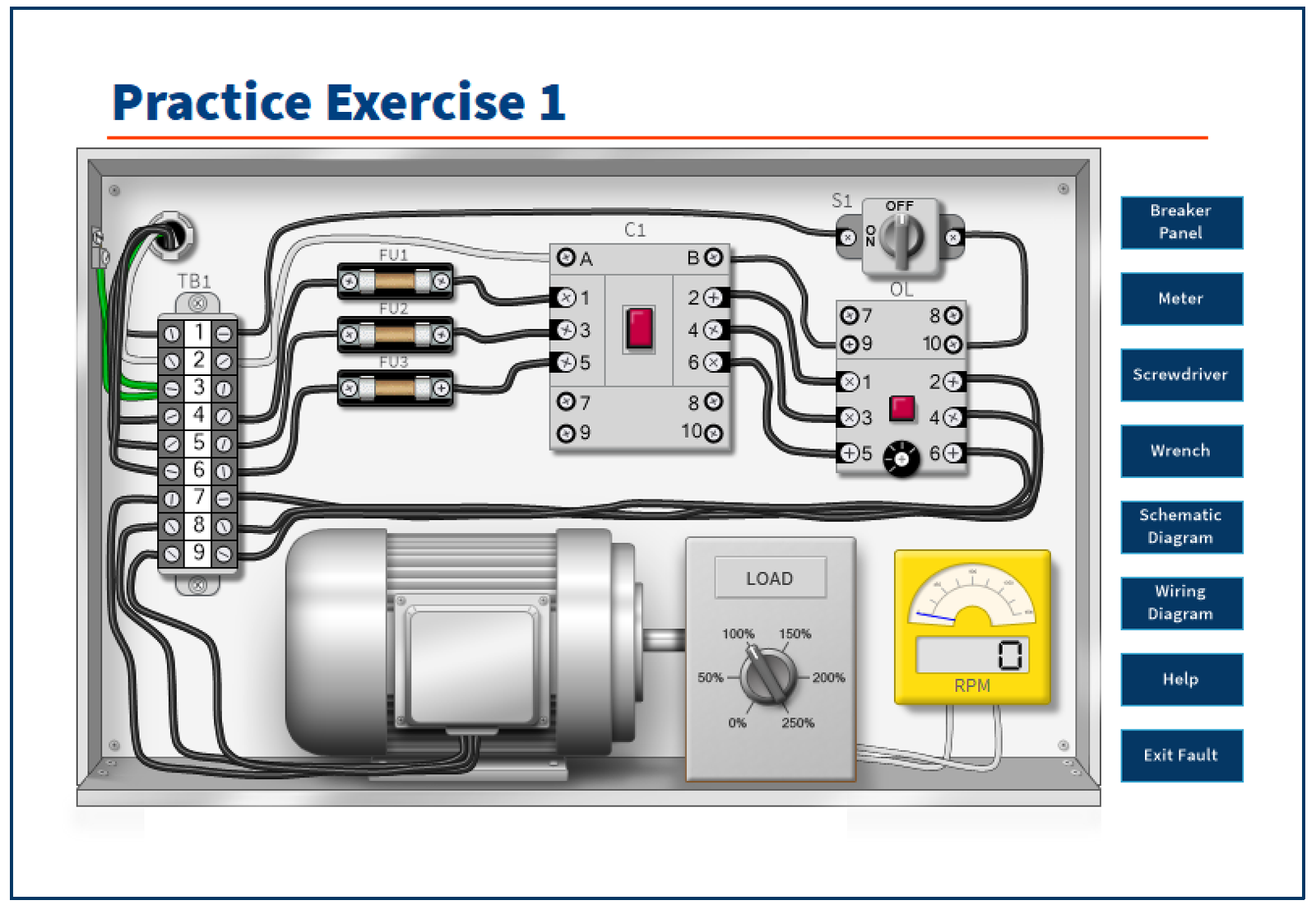
Troubleshooting Motor Circuits | Simutech Multimedia - Source www.simutechmultimedia.com
- Identify Symptoms: Recognising common symptoms, like tripped circuit breakers or blown fuses, guides the troubleshooting process.
- Test for Continuity: Using a multimeter, checking circuit continuity helps determine if current flows properly, guiding fault isolation.
- Examine Connections: Inspecting electrical connections for loose wires, corrosion, or damage aids in identifying potential short circuit causes.
- Trace Circuits: Mapping the circuit path allows for systematic testing and isolation of faulty components, helping locate the short circuit source.
- Inspect Insulation: Damaged or compromised insulation can lead to short circuits. Visual inspection and insulation resistance testing help detect these issues.
- Consider Overload: Assessing connected devices' power consumption and ensuring they do not exceed circuit capacity helps prevent overloads and subsequent short circuits.
By understanding these key aspects, electricians and electrical professionals can systematically approach troubleshooting electrical short circuits, ensuring electrical safety and resolving service disruptions efficiently. Timely detection and remediation of short circuits minimise potential electrical hazards, safeguard electrical systems, and maintain reliable power distribution.

Electrical Troubleshooting Plc Troubleshooting Training - Source fity.club
The Ultimate Guide To Troubleshooting Electrical Short Circuits
An electrical short circuit is a low-resistance connection between two points in an electrical circuit, which allows a large amount of current to flow through it. This can cause the circuit to overheat and potentially start a fire. Electrical short circuits can be caused by a variety of factors, including faulty wiring, damaged insulation, and loose connections.
Troubleshooting electrical circuits v4 crack - mzaerweed - Source mzaerweed.weebly.com
Troubleshooting electrical short circuits can be a complex and challenging task. However, by following the steps outlined in this guide, you can increase your chances of identifying and fixing the problem safely and effectively. In this guide, you will learn how to identify the symptoms of an electrical short circuit, how to locate the source of the problem, and how to repair the damage. You will also learn about the different types of electrical short circuits and how to prevent them from occurring in the future.
Electrical short circuits are a serious electrical hazard that can cause fires, injuries, and even death. It is important to be able to identify and troubleshoot electrical short circuits in order to keep yourself and your loved ones safe. By following the steps outlined in this guide, you can learn how to troubleshoot electrical short circuits safely and effectively.
| Type of Short Circuit | Description | Symptoms | Causes |
|---|---|---|---|
| Line-to-line short circuit | A short circuit between two live wires | A sudden drop in voltage, sparks or arcing, and blown fuses or tripped circuit breakers | Faulty wiring, damaged insulation, or loose connections |
| Line-to-neutral short circuit | A short circuit between a live wire and a neutral wire | A sudden drop in voltage, sparks or arcing, and blown fuses or tripped circuit breakers | Faulty wiring, damaged insulation, or loose connections |
| Line-to-ground short circuit | A short circuit between a live wire and the ground | A sudden drop in voltage, sparks or arcing, and blown fuses or tripped circuit breakers | Faulty wiring, damaged insulation, or loose connections |
| Neutral-to-ground short circuit | A short circuit between the neutral wire and the ground | A slight drop in voltage, no sparks or arcing, and no blown fuses or tripped circuit breakers | Faulty wiring, damaged insulation, or loose connections |